House Wren
General Description
The House Wren is a small, brown bird with few readily apparent field marks. It is slender and gray-brown, lighter in color overall and with a longer tail than the Winter Wren. Its wings and tail are mottled, but its back and belly are fairly clear.
Habitat
House Wrens inhabit gardens, hedgerows, brushy woods, wetlands, and other edges. They use a variety of habitats, as long as they have a dense shrub layer.
Behavior
The secretive House Wren hops about on the ground and in the low understory with its short tail held up. It often punctures the eggs of nearby nesting birds, both of its own and other species.
Diet
Crawling insects and spiders are the primary prey of House Wrens.
Nesting
These birds have a tendency to nest around human homes and in birdhouses, thus the name House Wren. The male defends its territory and attracts females by singing. The birds start a number of nests, and the female selects one to finish. They are usually monogamous, but the male may have more than one mate at a time, and the female may raise a second brood with a new mate, leaving her young for the first male to raise. House Wrens build their nests in cavities, both natural and artificial. The nests are usually near the ground, but may be high up in trees as well, especially in the mountains. The nest's foundation is a large pile of twigs, and the nest itself is a cup built of soft plant fibers, hair, and feathers. The female incubates 6 to 7 eggs for 12 to 15 days. Both parents feed the chicks, which leave the nest after 12 to 18 days.
Migration Status
Most House Wrens migrate to the southern United States or north and central Mexico for the winter. Some of Washington's birds move up-slope in late summer after the breeding season, and most have left Washington by late September. There are a few accepted records of House Wrens in southeastern Washington in the winter, but they were living in heated stock sheds. In the spring, males tend to arrive before females.
Conservation Status
House Wrens currently occupy the broadest latitudinal range of any native songbird in the New World. House Wrens have benefited from the fragmentation of forests across the United States, including Washington. This fragmentation increases the shrubby edge habitat that they prefer. They are fairly tolerant of human activity, which makes them well adapted to our increasingly developed landscape. They also seem to benefit from logging, using slash piles and small snags. In some areas in the 19th Century, there was a decline of House Wrens, which is blamed on the introduction of the House Sparrow because they compete for nesting cavities. In Washington and North America as a whole, the House Wren population has been on the rise since 1966, increasing an average of 8.3% per year in Washington and 1.6% per year in North America, based on Breeding Bird Survey data. This increase may be of concern since House Wrens destroy nests of other species, and compete with other, less common cavity-nesters.
When and Where to Find in Washington
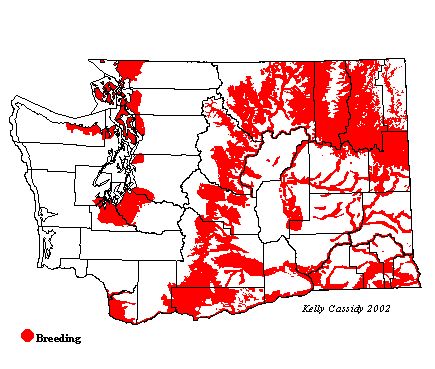
House Wrens are common and widespread from mid-May to the end of August at lower elevations in eastern Washington, outside of the hottest parts of the Columbia Basin. In western Washington, they are more scattered, common in the dry prairie habitat in the San Juan Islands (San Juan County), and uncommon in similar dry spots around Sequim (Clallam County) and Ft. Lewis (Pierce County). They are also uncommon in the summer in residential areas in Bellingham (Whatcom County), on Whidbey and Camano Islands (Island County), Everett and Marysville (Snohomish County), north Seattle (King County), and in the Nisqually National Wildlife Refuge (Thurston County). They are abundant breeders in Clark County, especially at the Ridgefield National Wildlife Refuge.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | R | R | R | R | ||||||||
| Puget Trough | R | F | F | F | R | |||||||
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | U | U | U | U | ||||||||
| East Cascades | F | F | F | F | F | U | ||||||
| Okanogan | U | C | C | C | C | U | ||||||
| Canadian Rockies | U | F | F | F | U | U | ||||||
| Blue Mountains | R | U | F | F | F | F | ||||||
| Columbia Plateau | F | C | C | C | C | C |
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map