White-winged Crossbill
General Description
White-winged Crossbills are finches with highly specialized, crossed bills and long, pointed wings. Male White-winged Crossbills are rosy-red with black wings and two white wing-bars. Females are dark greenish-yellow with black wings and white wing-bars. Juveniles are streaked brown, also with wing-bars.
Habitat
White-winged Crossbills are a far northern species, typically found in boreal forests with mature Engleman spruce and larch. They may also use western and mountain hemlock.
Behavior
White-winged Crossbills can be found in large flocks year round and call when they are foraging in an unproductive area. When many seeds are available they remain quiet. If only a few birds call, the flock continues to forage, but if a number of birds call, the flock will move on to find a more productive spot. Their bills are adapted for removing seeds from cones, and they start at the bottom of a cone and spiral upward, prying open each scale and removing the seeds with their tongues. The bills can cross in either direction, and the direction of the cross dictates the direction that the bird spirals up the cone. They can eat up to 3,000 seeds a day.
Diet
In Washington, White-winged Crossbills eat almost entirely Engleman spruce seeds.
Nesting
The breeding cycle of White-winged Crossbills is more closely tied to food availability than it is to season. They can breed at any time of year, often in mid-winter if there is an abundant source of seeds. They may be able to breed as young as five months old, and can have multiple clutches in a year. This results in a high reproductive potential. They are monogamous, and pairs form within flocks. The female builds the nest, which is typically on a horizontal branch high up in a spruce tree. The nest is an open cup of twigs, weeds, grass, and bark strips, lined with rootlets, lichen, moss, and hair. The female incubates 2 to 4 eggs for about 12 to 14 days. The male brings food to the incubating female and to the young for the first few days after they hatch. After about five days of continuous brooding, the female joins the male in bringing food to the young. The young leave the nest after about 18 to 22 days. Once the young fledge, the male may continue to care for them while the female begins a second clutch. The young birds' mandibles begin to cross about two weeks after they fledge, and they learn to extract seeds soon after that.
Migration Status
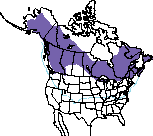
White-winged Crossbills do not undertake a regular migration, but do wander nomadically throughout their range and congregate in areas with large cone crops. Many of these movements occur in late October and November. Birds in the Pacific Northwest may travel as far as the northeastern United States in search of food, and birds from farther north may come into Washington in the winter when northern cone crops fail.
Conservation Status
Numbers in Washington are quite variable. White-winged Crossbills appear to come into the state when cone crops are low in other areas. They generally stay for a few years and move on when they have exhausted their supply of Engleman spruce cones. They have a high reproductive potential, however, and can recover quickly from losses when they find a new food supply. Forestry practices pose significant threats to the population. Most conifers do not produce suitable cone crops until they are 30 years old, and don't maximize cone production until they are 60 years old. Logging rotations need to be long enough to allow cone production in order to sustain White-winged Crossbills. Construction and maintenance of roads in forested areas also reduce habitat for these birds.
When and Where to Find in Washington
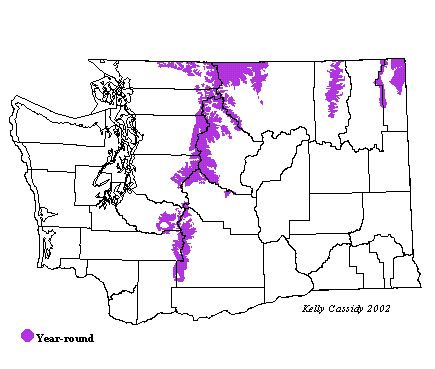
White-winged Crossbills are typical of areas farther north, and are rare in Washington. In many years, none are seen, while in other years there are large invasions, especially in the north Cascades and northeastern Washington in winter. They have probably bred in northeastern Washington and the north Cascades, perhaps even as far south as Mount Rainier.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | ||||||||||||
| Puget Trough | ||||||||||||
| North Cascades | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| West Cascades | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | |||||
| East Cascades | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| Okanogan | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| Canadian Rockies | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| Blue Mountains | I | I | I | I | I | I | ||||||
| Columbia Plateau |
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map

Family Members
 BramblingFringilla montifringilla
BramblingFringilla montifringilla Gray-crowned Rosy-FinchLeucosticte tephrocotis
Gray-crowned Rosy-FinchLeucosticte tephrocotis Pine GrosbeakPinicola enucleator
Pine GrosbeakPinicola enucleator Purple FinchCarpodacus purpureus
Purple FinchCarpodacus purpureus Cassin's FinchCarpodacus cassinii
Cassin's FinchCarpodacus cassinii House FinchCarpodacus mexicanus
House FinchCarpodacus mexicanus Red CrossbillLoxia curvirostra
Red CrossbillLoxia curvirostra White-winged CrossbillLoxia leucoptera
White-winged CrossbillLoxia leucoptera Common RedpollCarduelis flammea
Common RedpollCarduelis flammea Hoary RedpollCarduelis hornemanni
Hoary RedpollCarduelis hornemanni Pine SiskinCarduelis pinus
Pine SiskinCarduelis pinus Lesser GoldfinchCarduelis psaltria
Lesser GoldfinchCarduelis psaltria American GoldfinchCarduelis tristis
American GoldfinchCarduelis tristis Evening GrosbeakCoccothraustes vespertinus
Evening GrosbeakCoccothraustes vespertinus

